Incremental Encoder vs Absolute Encoder Differences and Selection Guide
Discover the key differences between incremental and absolute encoders including performance, cost, and application tips for precise motion control.
Read More
In today’s world of industrial automation and smart manufacturing, encoders play an essential role. They help machines “see” position and movement, making precise control and feedback possible. Whether it’s a robot, CNC machine, or automated production line, encoders are key sensor devices.
As a professional encoder supplier, we understand that every customer has unique needs. Choosing the right type of encoder directly impacts your equipment’s performance and reliability. This article will introduce the main types of encoders, helping you quickly understand their features and applications, so your B2B selection process is more scientific and efficient.
There are many types of encoders, and they can be categorized in several ways. Understanding these categories helps you quickly find the right product.
By Motion Type
By Output Signal
By Sensing Technology
These categories not only help you understand how encoders work but also make it easier to choose based on your needs.
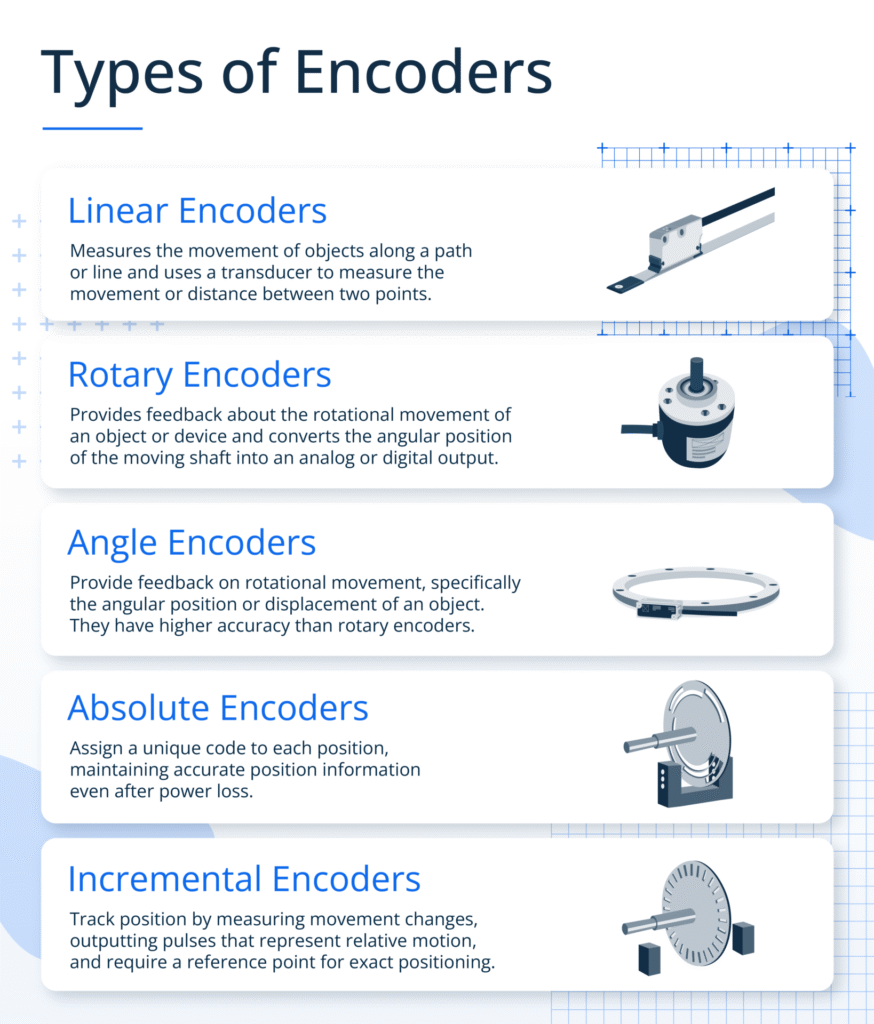

Rotary encoders are the most common type. They measure the rotation angle or speed of a shaft and are widely used in robotic joints, automation devices, and motor control.
Linear encoders measure straight-line displacement. They’re commonly found in CNC machines and measuring instruments, providing high-precision position feedback to ensure processing accuracy.
Incremental encoders output pulses to reflect position changes. They have a simple structure and lower cost, but position data is lost when powered off. They suit cost-sensitive applications where real-time compensation is possible.
Absolute encoders provide unique position information, which is not lost during power outages. They are ideal for industrial environments that require power-off protection and high reliability. Single-turn and multi-turn versions are available for different measurement ranges.
Optical encoders use optical sensing technology. They offer high accuracy and resolution but are sensitive to dust and vibration. They’re best for clean environments and high-precision requirements.
Magnetic encoders detect position changes via magnetic fields. They have strong anti-interference capabilities, making them suitable for harsh environments with high temperatures, dust, or vibration.
These encoders have a complex structure and are suitable for extreme environments with strong anti-interference features. They’re often used in aerospace, heavy machinery, and other specialized industries.
| Encoder Type | Accuracy | Environmental Adaptability | Cost | Maintenance | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optical Encoder | High | Average | Medium-High | Medium | High-precision machinery, robotics |
| Magnetic Encoder | Medium | Strong | Medium | Low | Harsh environments, industrial automation |
| Incremental Encoder | Medium | Average | Low | Low | Speed feedback, general automation |
| Absolute Encoder | High | Strong | High | Medium | Power-off protection, high-reliability uses |
| Linear Encoder | High | Average | Medium-High | Medium | CNC machines, measuring instruments |
| Inductive/Resolver Encoder | Medium-High | Very Strong | High | High | Aerospace, heavy machinery |
Don’t just look at the price when choosing an encoder! Ask yourself a few questions first:
With these questions in mind, you can narrow down your options. For example:
Also, consider interface compatibility, resolution, installation method, and customization options. Our factory offers a wide range of encoder products and custom solutions—feel free to contact us for expert advice!
Choosing the right encoder is key to ensuring equipment performance and production efficiency. Understanding the main types and features of encoders helps your B2B project avoid detours and boosts your overall competitiveness.
If you’re looking for high-quality, reliable encoders, visit our website or contact us directly. Our professional team will tailor the most suitable solution for you and help upgrade your industrial automation!
Common issues include signal loss, position drift, and mechanical wear. Regular maintenance and choosing the right encoder for your environment can greatly reduce failure rates.
If you need to retain position after power loss, absolute encoders are best. Incremental encoders are suitable for real-time monitoring and cost-sensitive applications.
Encoders output digital signals directly, offering high precision and fast response—ideal for dynamic control. Other sensors, like potentiometers, are more for simple position detection.